Evaporative Condensers: Maintenance and Operation
The essence of the evaporative condenser is evaporation: Heat rejection occurs when water is sprayed on the external surface of coolant tubing. The process of evaporation that takes place on the external surface of the tubing cools the refrigerant within. Oftentimes the cooling transforms the refrigerant from a liquid to a gas, and cooling transforms it back to a liquid. Sometimes the evaporation merely cools fluid flowing through the tubes.
When super-heated refrigerant is inside the tubing, it means that evaporative condensers run at very high skin temperatures, and they need special attention.
An effective water treatment program is crucial on systems that run high skin temperatures. If anything impedes the water from flowing, such as scale, leaves or other debris, cooling will be impaired. The system can fail to maintain process temperatures at the optimal range, which may interfere with production. Ultimately, serious system damage can result.
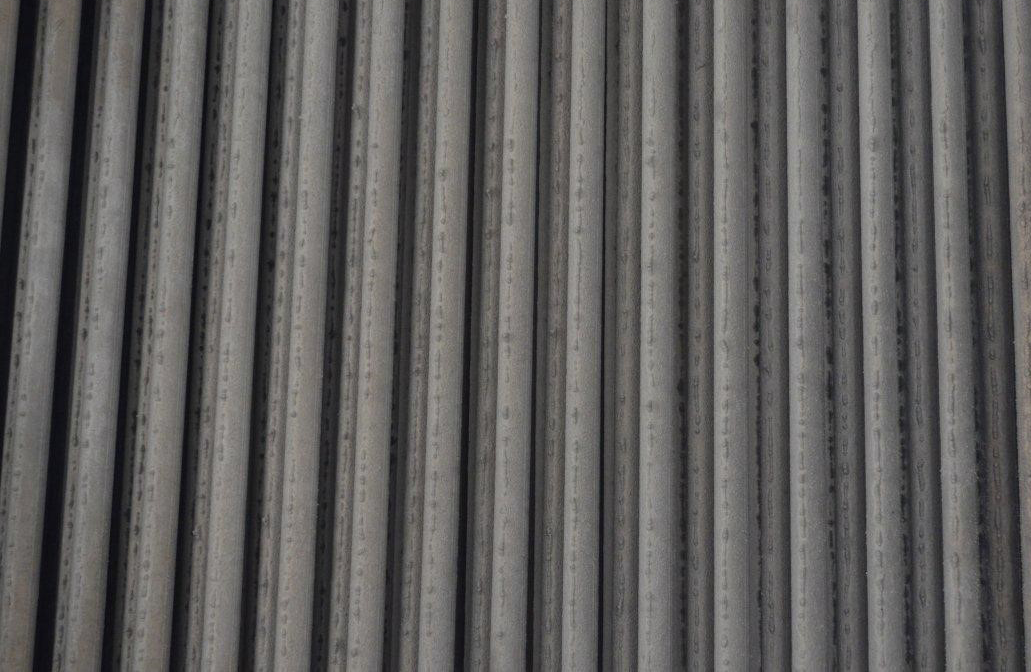

Ensuring Water Flow in Evaporative Condensers
Chemical maintenance includes using a high stress water treatment chemical, these chemistries can endure the demands of high skin temps.
Because water flow is crucial in the prevention of scale in these systems, physical maintenance includes:
- Clean pump suction screens to ensure maximum flow.
- Check and clean spray nozzles to ensure free water flow and uniform coverage.
- Maintain system fans to ensure temperatures do not exceed 100oF.
Properly designed water treatment chemistry and adhering to a preventative maintenance program are crucial for the proper operation of evaporative control systems to extend the life of the equipment and get maximum efficiency.
Chemtex is always standing by to respond to your questions, troubleshoot your problems, and help you build a water treatment program that is optimized to maintain the lifespan of your expensive equipment.



/NQA-ISO-9001-Logo-ANAB.jpg)